Table of Contents
Evidence Based Treatment Therapy is a popular term in the mental health and substance addiction recovery community that it is often thrown around without any explanation as to what it means.
While the name “evidence based treatment” provides a clue, the details often get lost or go unexplained to the people who are seeking treatment.
With so many different types of addiction programs, it’s difficult for an individual to find the most appropriate one for his or her needs, and even harder to find a suitable facility for someone they care about.
It’s estimated that only 10 percent of recovery programs utilize evidence based substance abuse treatment. It is highly successful and is most often used by non 12 step rehab facilities.
What is Evidence Based Treatment?
At its most basic level, evidence based treatment can be defined as therapies and methods that have shown to be successful for addiction recovery according to research and scientific testing methodologies.
Evidence Based Treatment (EBT), sometimes referred to as “science based therapy” or “evidence based practices” (EBP), originated in the medical field in the 1980s, but didn’t gain popularity until the 1990s when the term was more widely used.
In the early 2000s, treatment models based on evidence from scientific research expanded to other fields, including mental health and substance addiction treatment.
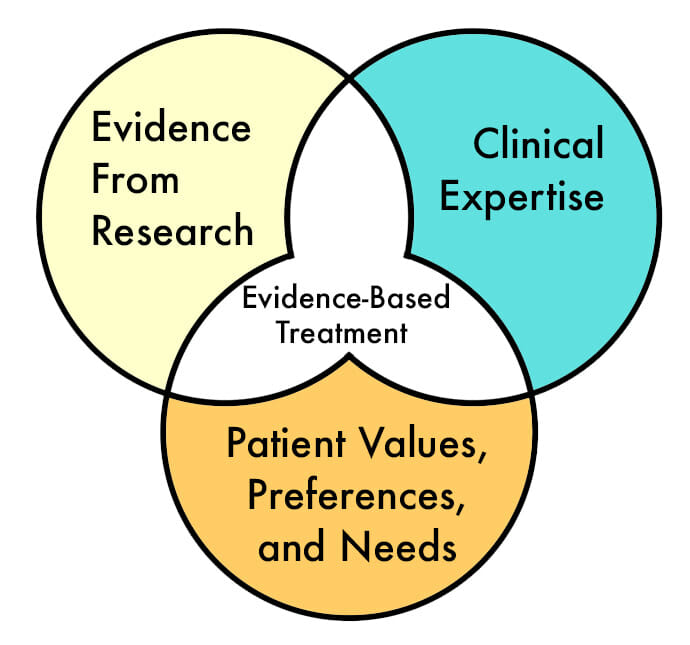
Evidence based treatment practices integrate the following:
1. Evidence From Research
This involves using evidence based treatment methods that are backed by research that has shown them to be effective for recovery.
2. Clinical Expertise
Patients are in the care of trained professionals who provide a proper clinical assessment and specialize in the treatment methods necessary for recovery.
3. Patient Values, Preferences, Needs, and Goals
Each patient’s individual needs and goals are considered with respect to treatment for their specific condition. This includes age, gender, environmental issues, readiness to change, and other personal factors that have a positive impact on recovery.
The American Psychological Association states that evidence based practices integrate “the best available research with clinical expertise in the context of patient characteristics, culture, and preferences.”
The decision-making process provides a framework for the best treatment model for each patient’s recovery and specific condition.
Evidence based therapy practices involve conducting clinical assessments, referencing research, collaborating with the patient, and using treatment therapies that have proven to be successful for a particular condition.
Evidence Based Treatment Therapies
Evidence based treatment therapies are effective for addressing a wide range of disorders such as PTSD, anxiety, depression, drug or alcohol addiction, and co-occurring disorders of mental health and addiction together.
These therapies can be short-term interventions that run for a specified number of sessions or weeks, although many patients find the most success with a comprehensive program that lasts 90 days or more for some conditions.
Treatment can be done with individuals, families, or groups, depending on the therapies needed and the specific model of recovery.
Evidence based therapies can be provided in different settings, such as an outpatient clinic or a residential treatment facility.
Once mastered, a patient can continue to use the tools and techniques learned from these therapies at home after a formal treatment program has been completed.
Many treatment modalities can be useful for everyone, although some need to be adapted for certain age groups.
Common evidence based treatment therapies include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Motivational Enhancement Therapy or Motivational Interviewing
- Relapse Prevention Therapy
- Contingency Management (CM)
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
- Medication Assisted Treatment (MAT)
- Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT)
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
- Internal Family Systems Therapy (IFS)
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
- 12 Step Facilitation Therapy
Most evidence based therapies require extensive training to properly implement specific interventions using different steps and tools. This allows practitioners to guide interventions in a consistent and systematic manner.
Medication Assisted Treatment uses evidence based pharmacotherapies. These are medications that help withdrawal symptoms during detox, and others like Methadone or Suboxone to reduce cravings for opioids. There is much research to support the efficacy of these types of interventions.
Many of the others listed above are evidence based behavioral therapies that have proven through research and scientific studies to work well for alcohol addiction treatment, drug addiction, PTSD, and related mental health conditions.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most well-known and widely used evidence based therapies for mental health and addiction recovery.
One of the goals of cognitive behavioral therapy techniques is to understand the relationship between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. Changing negative thought patterns to positive ones will improve mood, emotions, and lead to healthier behaviors.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is like CBT and is beneficial for many conditions. DBT Therapy techniques are useful for managing unhealthy emotions, and coping with stress, anxiety, and interpersonal relationships.
Relapse Prevention Therapy helps recognize triggers that might cause a person to begin using substances again and teaches techniques to remain abstinent.
Internal Family Systems Therapy (IFS) is an individualized form of psychotherapy between a therapist and patient. IFS Therapy promotes trust and healing for mental health and substance addiction recovery.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a mindfulness-based therapy that does not try to control or change painful emotions. Instead, acceptance and commitment therapy exercises utilize six core processes that teach techniques to stop denying or avoiding painful emotions.
Some of these therapies are specific to certain conditions, while others work for a range of conditions, and can be used to complement each other.
Components of Evidence Based Therapy Models
While all recovery models will vary, there are core components that can be found in many. Because they are time-limited, the models are designed to equip patients with the necessary skills to manage their wellness over time.
Psychoeducation
Psychoeducation presents information relevant to a patient’s health issues to gain insight into triggers, warning signs, and symptoms. The intent is to promote self-awareness, identify personal needs, and address problems as they arise.
Skills Training
Patients learn how to manage their symptoms using appropriate coping mechanisms and distress-tolerance skills. They practice these skills on a consistent basis during calm periods to be better prepared in the presence of triggers.
Maintenance and Relapse Prevention
Once patients demonstrate a consistent relief of symptoms, they prepare for termination. By this time they should have the skills to independently manage their symptoms.
Goal of Evidence Based Treatment
While evidence based treatment methods are backed by research, not every treatment approach is going to work for everyone. There is no such thing as a one-size-fits-all treatment approach, but there are many options available, especially as more models emerge.
The ultimate goal of evidence based therapy is to provide effective treatment methods that allow each patient to experience a lifelong recovery.
With that said, recovery may look different to each person depending on many factors. Relapse is a common component of addiction that affects some individuals and not others.
Even if a person does relapse, it should not be considered a failure. Recognizing it happened and getting back on track is an important part of recovery.
Evidence based treatment aims to improve a person’s quality of life, physical and mental health, and personal relationships. It also strives to reduce risky behaviors that may lead to unwanted consequences.
There is a consensus among treatment providers about what works well based on research and past experience, with new methods being developed and tested all the time.
As the evidence deems new approaches to be effective, they will no doubt be adopted for use as another successful recovery tool.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do evidence based treatments improve recovery outcomes for addiction and mental health?
Evidence based treatments improve recovery outcomes because they are scientifically validated, adapted to individual needs, focused on skill-building, and regularly evaluated for effectiveness.
The benefits include holistic nature of treatment, faster relief of symptoms than from other therapies, lower relapse rates, and enhanced sustainability.
Key points about evidence based therapies:
- Scientifically proven through research to be effective
- Flexible and individualized to each person’s needs
- Focused on teaching coping skills
- Progress is measurable and trackable
- Integrates medication and therapies to enhance recovery
- Comprehensive and holistic
- Higher acceptance rates by insurance providers
What is the APA list of evidence based treatments?
The American Psychological Association (APA) regularly updates a list of evidence based treatments that meet the proper research criteria.
Treatment therapies are evaluated using the Chambless & Hollon (1998) criteria and Tolin (2015) criteria.
The current list of evidence based psychological treatments is searchable by disorder and can be found on the Society of Clinical Psychology (APA Division 12) web page.
What are the most effective behavioral therapies supported by research for substance use disorders?
Several behavioral therapies have been proven by research to be effective for treating substance use disorders and addiction. These include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Motivational Enhancement Therapy (MET)
- Family Therapy
- 12-Step Facilitation
These therapies enhance motivation, teach coping skills, help prevent relapse, involve family members, and provide positive reinforcement, peer support, and group participation.
Combining these behavioral therapies with medication assisted treatment has shown to improve recovery outcomes.
Is Medication Assisted Treatment an evidence based therapy?
Yes, Medication Assisted Treatment (MAT) is an evidence based therapy for substance use disorders and addiction.
It is a comprehensive and integrated approach that combines FDA-approved medications with counseling, behavioral therapies, and peer support.
What is the most effective evidence based treatment for opioid use disorder?
The most effective treatment approach for addiction to opioids, heroin, and fentanyl is a combination of Medications for Opioid Use Disorder (MOUDs) and evidence based behavioral therapies.
MOUDs are a form of Medication Assisted Treatment backed by research and supported by treatment providers and major health organizations.
Medications for Opioid Use Disorder include Suboxone, Methadone, Buprenorphine, and Naltrexone. They can be used during detoxification and long-term treatment to reduce cravings and prevent relapse.
Is Mindfulness an evidence based treatment?
Yes, Mindfulness is an evidence based treatment therapy for addiction and many types of mental health conditions.
Several forms of specialized mindfulness therapies include:
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT)
- Mindfulness-Based Relapse Prevention (MBRP)
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR)
Mindfulness therapy has proven to be valuable for reducing stress, anxiety, depression, relapse rates, and substance cravings.